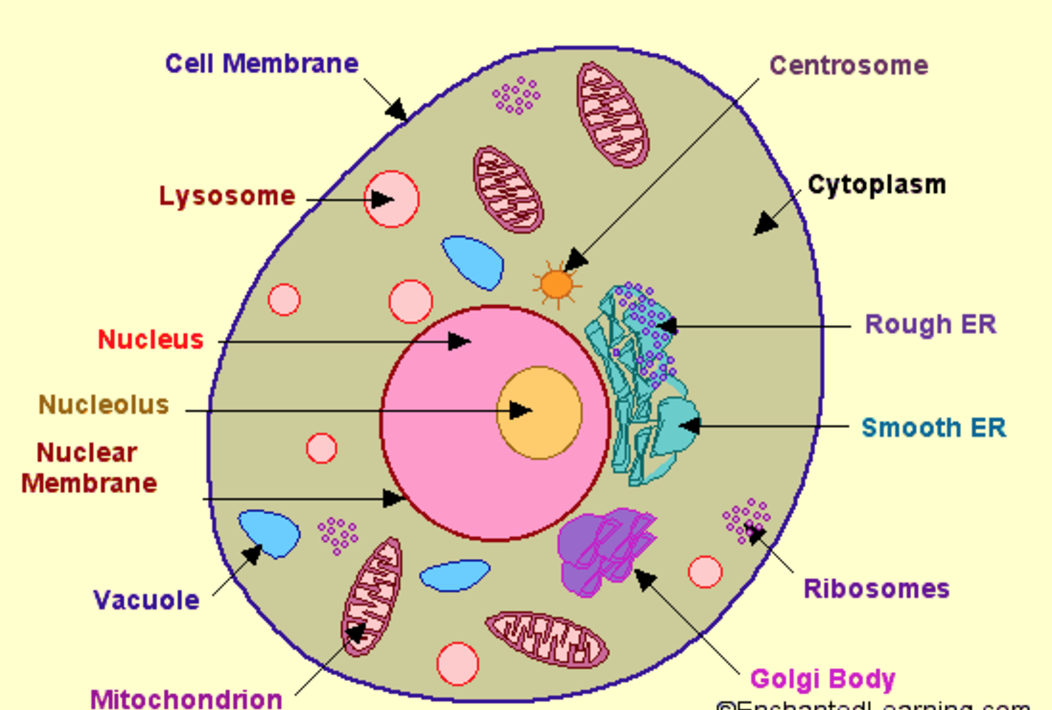
[DIAGRAM] Parts Of A Cell Diagram
Cell types Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possesses a nucleus, and prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but still has a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled or multicellular. [15] Prokaryotic cells Structure of a typical prokaryotic cell
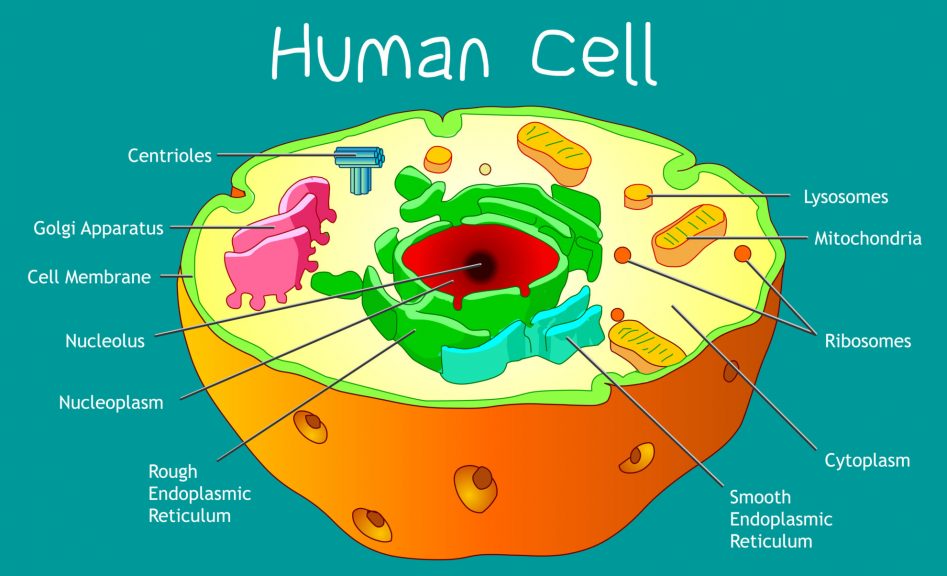
Cell Membrane Definition Biology Functions Cell Diagram
The type of cell that accounts for 90-95 percent of your skin are keratinocytes. Instead of being round and blob-like, their shape has a flake-shape than anything else, creating a mosaic of skin. They grow and divide in the basement membrane, a thin layer that separates your epidermis from your dermis. There they push toward the top of your skin.
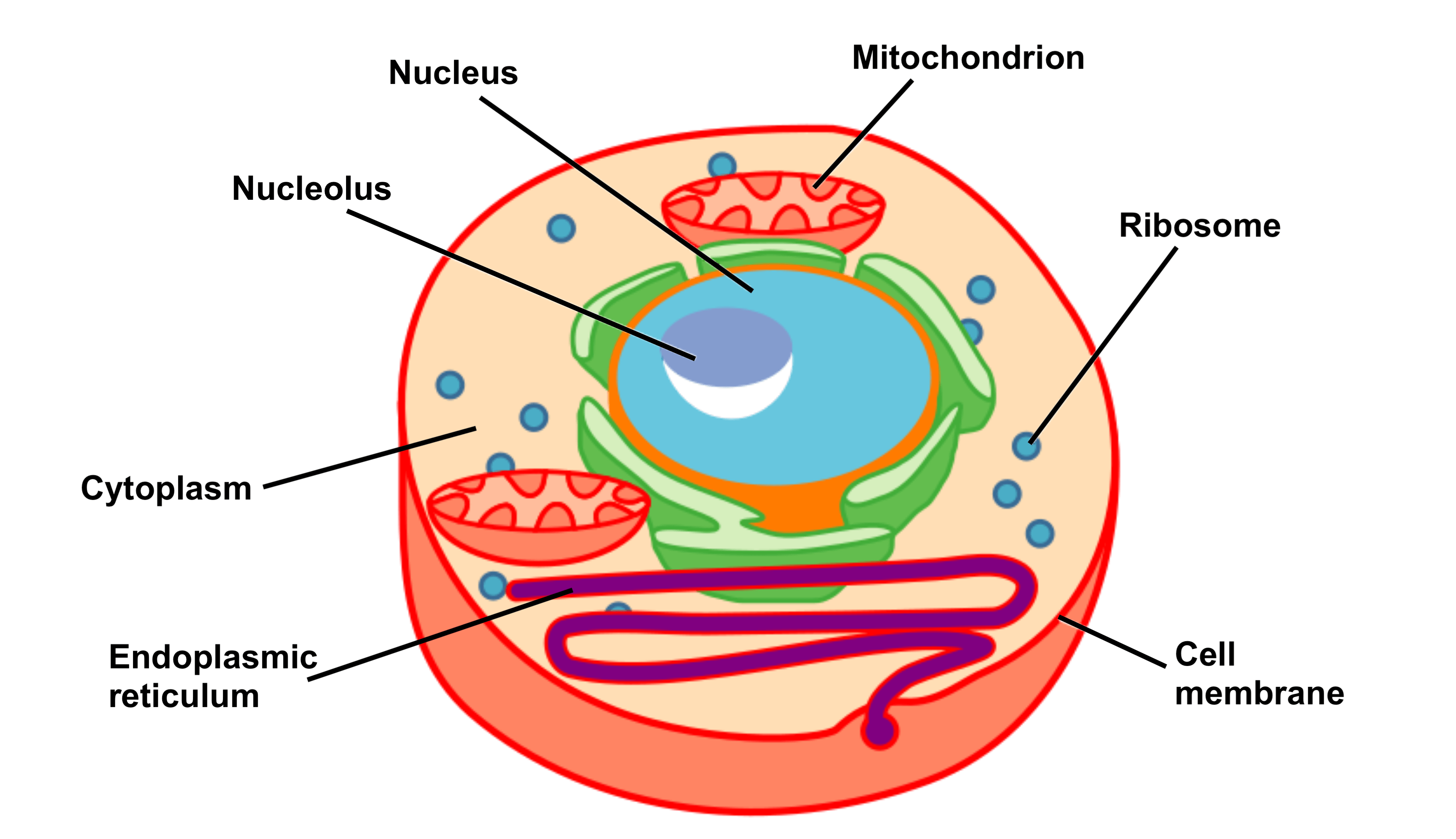
Cell Structure and Function Part 1 The Organelles Medical Exam Prep
A cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism, and all living structures in the human body are made of cells. There are hundreds of different types of cells in the human body, which vary in shape (e.g. round, flat, long and thin, short and thick) and size (e.g. small granule cells of the cerebellum in the brain (4 micrometers), up to the huge oocytes (eggs) produced in the female.
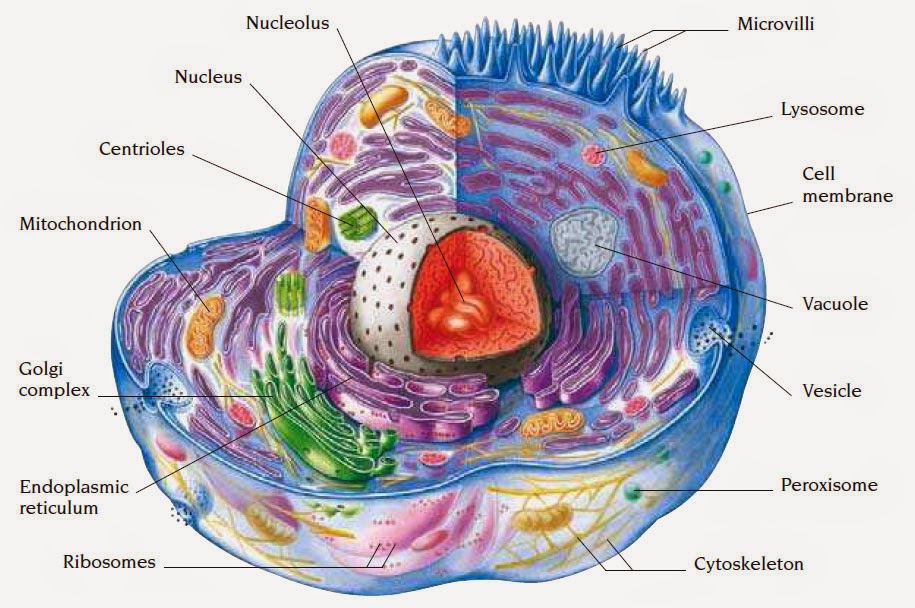
Cell Nursing
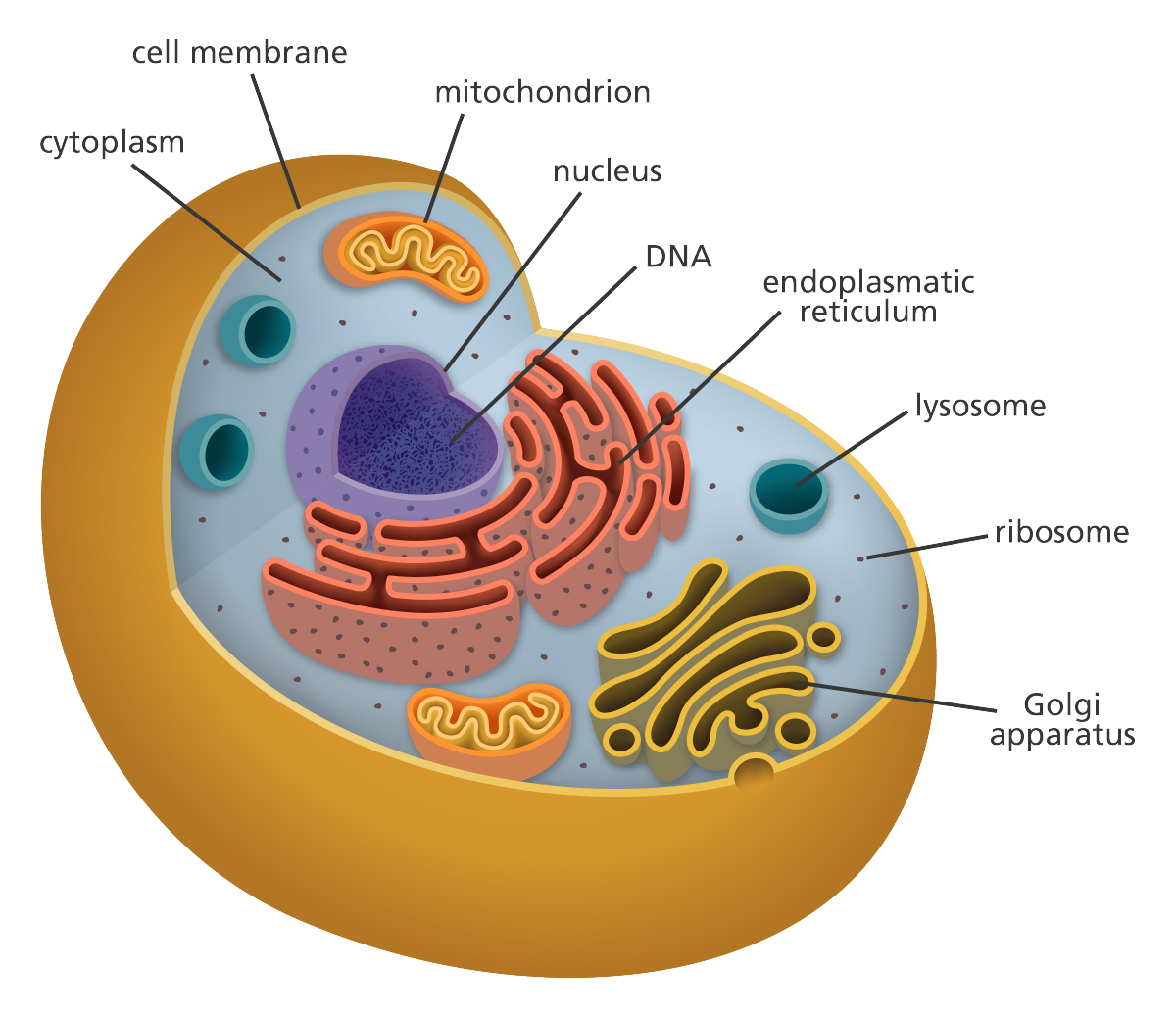
Diagram 1: The anatomical presentation of the human cell. Picture Source: www.printablediagram.com How many cells are in the human body ? Ans : Approx. 37.2 trillion cells What are the different parts of the human cells? How do these parts function? Cell membrane It is the outer covering of the cell, which consists of proteins and lipids.

69,023 Human Cell Structure Images, Stock Photos & Vectors Shutterstock
Interactive guide to stem cells and cell biology with 3D models and real microscopy data of GFP labeled hiPSCs.

Labeled Diagram Human Cell
The Human Cell Atlas is an international collaborative consortium that charts the cell types in the healthy body, across time from development to adulthood, and eventually to old age. This enormous undertaking, larger even than the Human Genome Project, will transform our understanding of the 37.2 trillion cells in the human body..

Infographic Anatomy of a Cell
Division and differentiation in human cells When cells express specific genes that characterise a certain type of cell we say that a cell has become differentiated. Structure and replication of DNA
The Cell Theory & Structure HubPages
Cell Structure Ideas about cell structure have changed considerably over the years. Early biologists saw cells as simple membranous sacs containing fluid and a few floating particles. Today's biologists know that cells are infinitely more complex than this. There are many different types, sizes, and shapes of cells in the body.
Human Cell Diagram 6406474 Vector Art at Vecteezy
The Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) is one of the most abundant proteins within the erythrocyte membrane and is required for glucose and dehydroascorbic acid (Vitamin C precursor) transport. It is widely recognized as a key protein for red cell structure, function, and metabolism. Previous reports highlighted the importance of GLUT1 activity within these uniquely glycolysis-dependent cells, in.
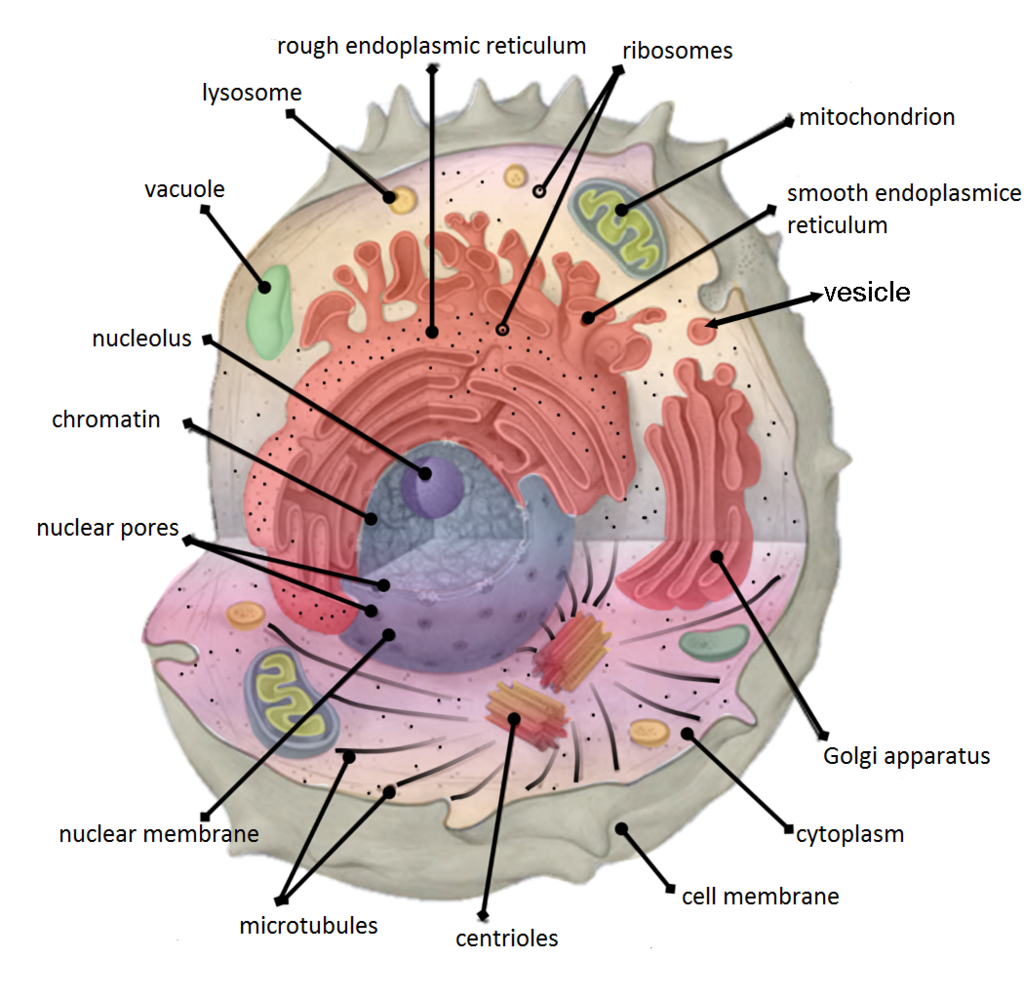
4.5 Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton Human Biology
Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell's parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.

The Human Cell Atlas An international effort
A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. Cells have three parts: the membrane, the nucleus, and the.
generalized human cell, labeled Diagram Quizlet
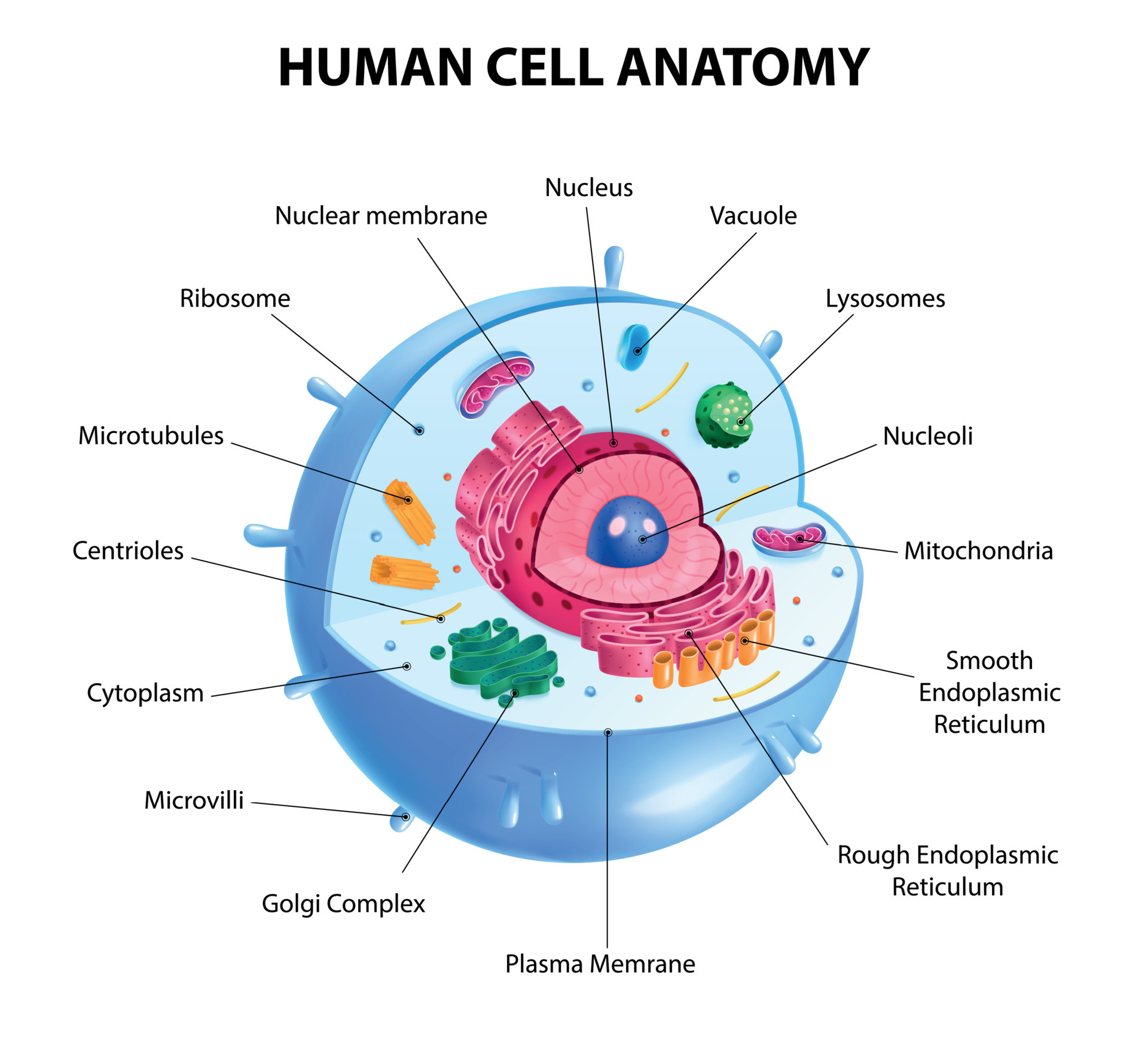
Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions The cell is the basic functional in a human meaning that it is a self-contained and fully operational living entity. Humans are multicellular organisms with various different types of cells that work together to sustain life.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12788/histology-eukaryotic-cell_english.jpg)
human cell diagram with labels
Muscle tissue is made up of cells that have the unique ability to contract or become shorter. There are three major types of muscle tissue, as pictured in Figure 10.3.14 10.3. 14: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissues. Skeletal muscles are striated, or striped in appearance, because of their internal structure.
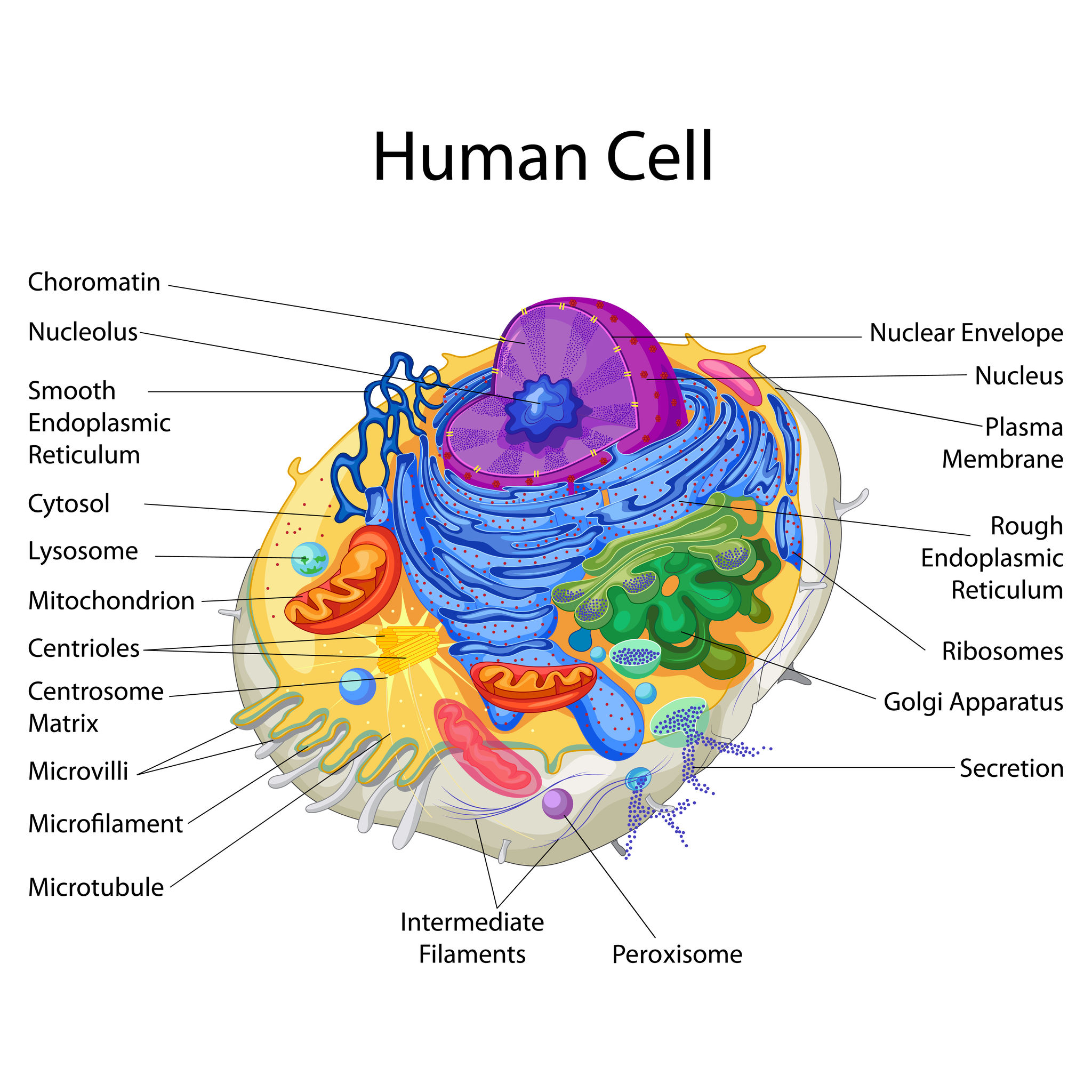
Education Chart of Biology for Human Cell Diagram Best Acupuncture llc
A human cell diagram provides a visual representation of the different components and organelles within a cell. An unlabeled human cell diagram, in particular, offers an excellent learning tool for students and researchers, encouraging them to identify and label the various parts independently.
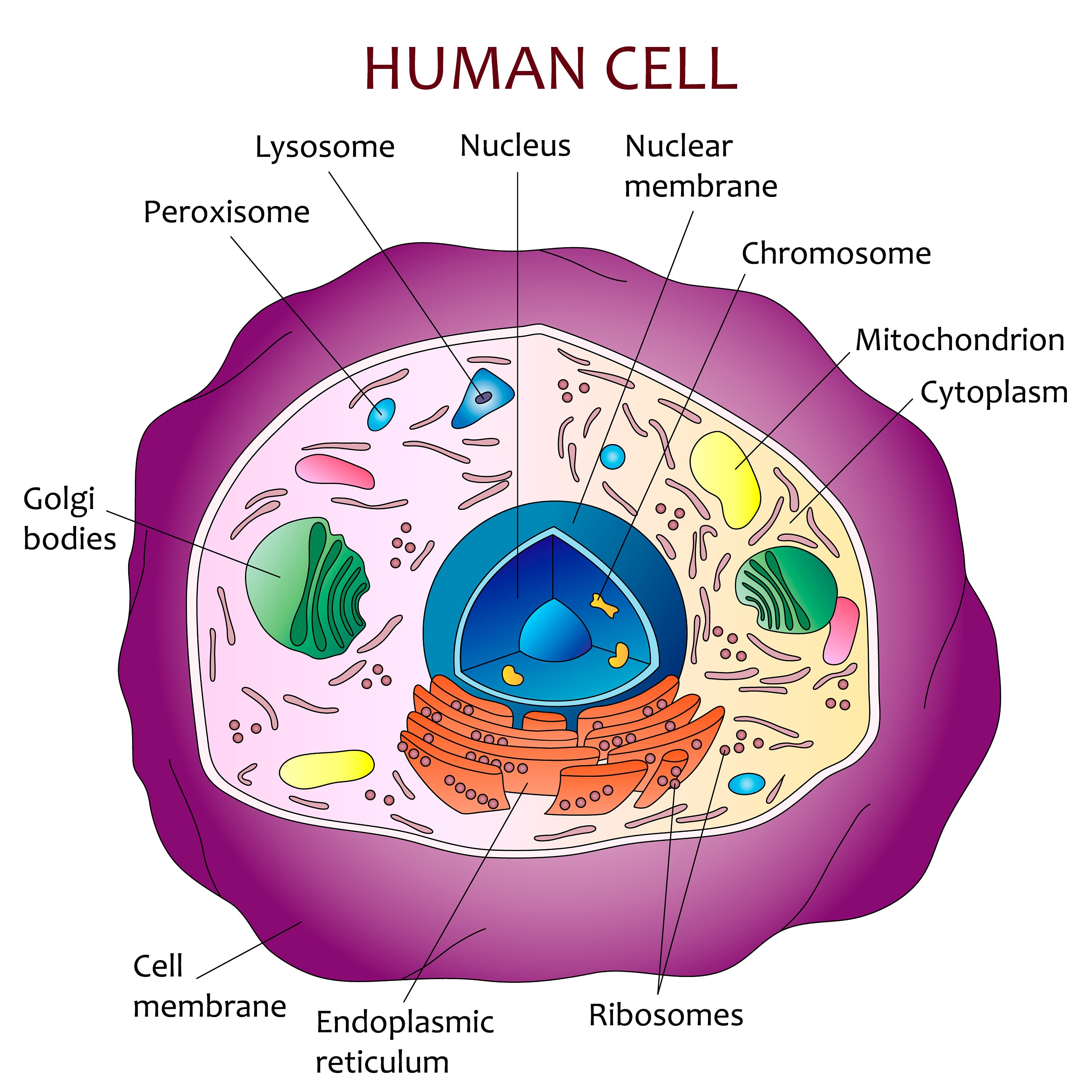
Human cell diagram Etsy
Cells of humans typically have a mass 400,000 times larger than the mass of a single mycoplasma bacterium, but even human cells are only about 20 μm across. It would require a sheet of about 10,000 human cells to cover the head of a pin, and each human organism is composed of more than 30,000,000,000,000 cells.

Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions Diseases Pictures
It consists of 258,385 cells from 14 different classes, with a large variation in the number of cells per class, ranging from as low as 323 cells to as high as >47,000 cells.